Features of the choice of greenhouses to give

For growing seedlings, early vegetables and greens in an unfavorable climate in central Russia, summer residents use various types of covering structures. Small buildings with a height of up to 1.3 meters and a width - within the ordinary beds for 2 rows of cucumbers, are called greenhouses.
Determine the purpose
First of all, it is necessary to identify the main characteristics of the greenhouse and its differences from the greenhouse. Capital buildings, called greenhouses, reach a height of over 2.5 meters and of such width that agricultural machinery can move between the rows. It is the size of greenhouses that differ from greenhouses in the first place. Usually, greenhouses are first built on the newly emerging garden plots: the costs are small, the device does not need much time.
In addition to size, greenhouses and greenhouses differ from each other predominant set of crops grown in them. The separation is conditional, but still there are plants that are completely unsuitable for growing in a greenhouse.
For example, it is impossible to plant seedlings of tomatoes in a greenhouse to a permanent place, the height of which can reach 2 meters. The height of this structure is rarely even 1.3 meters.
In a small building it is possible to grow only tomatoes of low-growing varieties suitable for open ground. But these varieties like fresh air and do not tolerate high humidity, so they need not stationary hotbeds, but portable ones. They are installed on the beds in adverse weather, and in good - fully or partially understood. To obtain a rich crop of tomatoes in the open ground, gardeners often use greenhouses made of wire arcs and a covering film. In them, due to the small volume, a comfortable microclimate is quickly created for intensive growth and development of plants.
The period of use of greenhouses is significantly less than that of greenhouses, especially heated ones. Greenhouses at the end of the summer season are usually disassembled, and are set in place after thawing and drying out of the soil in spring.Heated greenhouses are operated all year round, the use of unheated facilities begins much earlier than greenhouses, they are not disassembled for the winter, and if they are dismantled, they are partially (for example, removed the film).
But greenhouses have their advantages: they quickly warm the earth and establish the necessary microclimate for the rapid development of plants. Humidity and temperature in greenhouses in early spring in good weather are ideal for growing greens, zucchini and cucumbers.
Greenhouses are most often used for growing seedlings and early greenery. They also feel comfortable cucumber planting, zucchini, squash and peppers. The owners of the cottages themselves need to decide for which crops it is most effective to use greenhouses. The following subjective factors play a significant role in the selection: the climatic zone of residence, a set of desired vegetables and greens, personal yield requirements, and financial possibilities of the family.
Kinds
One of the main advantages of greenhouses for gardeners - their quick, low-cost device on their own. The base is made on a flat platform of boards in the form of a rectangle with a given length and width.To this base is then attached frame. The frame can be made of wooden bars of various shapes (quadrangular with one slope or gable, arched of bent metal or synthetic pipes). These types of structures are usually covered with a film cover.
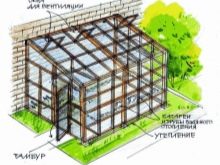
There are also greenhouses with a foundation buried in the ground. In this case, a ditch up to half a meter is pulled out in place of the greenhouse, and opening or removing frames are installed on top. These frames are made of wooden or profiled light metal in the form of a horizontal or with a slight inclination of the windows laid.
Modern factory greenhouses are often equipped with self-opening vents and even whole frames. Such devices, operating on temperature, are the key to saving the plants from overheating during the absence of owners in the country.
The fantasy of the owner of a dacha is often limited by the availability of improvised material. If financial capabilities allow, then you can purchase some ready-made parts of the future greenhouse, or even a completely factory product that satisfies your own material requirements, optimal dimensions and functionality.But it is not always possible to find such an ideal structure, so most gardeners are starting to build their own version of a protected garden bed.
Materials
A small or large greenhouse consists of:
- grounds;
- frame;
- cover.
In the ubiquitous structures of the arcs there is no foundation. Arcs are stuck in the ground for stability and covered with a film. In hot weather, the coating is removed, and in bad weather - back into place. If it is warm and there is no scorching sunlight, then it is enough to lift the film from the ends for airing. The arcs that make up the frame can be made of thick steel wire (6 mm thick), electrical aluminum conductors, pipes made of metal or polymer, and also curved from the rods of hazel or willow.
Grounds for serious structures are made of wooden boards, beams, thin logs, metal products (corners, profiles). Wooden materials are processed to protect against moisture with linseed oil, used car oil, sealants and antiseptics. Metal constructions are primed and painted. All these measures are necessary to extend the life of facilities.
The frame may be of the following types:
- frame;
- tunnel;
- lean-to;
- gable;
- wall mounted.
The most common material for all types of frame (except the tunnel) - wood. Some factory products are made of steel or aluminum elements. Tunnel greenhouses are made of metal or polymer arcs (bent pipes).
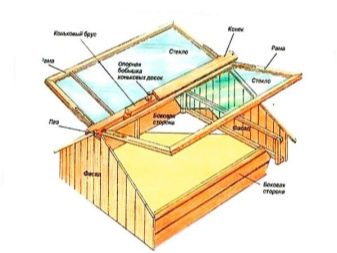
Wooden frames - the most time consuming to manufacture and has more than a dozen constructive forms. Among them: triangular, inclined with one slope, wall, attached to the greenhouse or house, gable, frame. In industrial production for dachas, even the names of samples give an idea of their forms: “butterfly”, “bread box”, “cabriolet”.
The choice of covering material for greenhouses is wider than for greenhouses.
- Glass in frame types of constructions. The frames in this case are mostly wooden.
- Polyethylene film. It is used for tunnel coatings, as well as in frame and other types of frame. But it does not differ in strength, therefore it needs annual renewal, which is troublesome. It is best to use a simple film for primitive devices under arcs.
- Reinforced plastic film. Durable covering material compared to conventional film. But the price has a corresponding.
- Cellular polycarbonate. This two-layer plastic material with an air gap is not afraid of hail or wind and retains heat well. The transparency is not inferior to glass and film. Suitable for stationary greenhouses that do not need to be cleaned for the winter.
For your own greenhouses, you need to choose the materials that are available on the farm and more fully meet the plans for vegetable production on their own plot. If you build light greenhouses, then you should not acquire for them an expensive covering material. Disassembling or storing them somewhere in the barn for the winter will result in damage to the cover.
For capital devices, it is better to purchase glass / polycarbonate that can withstand the snow load in winter. Usually good greenhouses pay for themselves within 3 seasons, and then for a minimum of 10 years they give only profit.
Dimensions
Ready-made greenhouses of even one model can have several modifications with different sizes: height - from 70 to 140 cm, width on average - 130 cm, and length - from 1.6 to 6 m.Frames for submerged structures rarely rise above the soil surface by more than 50 cm.
Self-made devices for protected ground are designed to any size.The basis of which is taken as usual for the local standards of the parameters of the beds. It depends on the type of crop that is planned to be grown in the greenhouse and its agronomical cultivation (how many rows in the bed, recommended distances between rows, plant height, density of bushes, the desired amount of crop, methods of processing beds and irrigation techniques).
Shelters of the tunnel type are arranged on the beds of a width not exceeding 1.5 m and the height of the arcs up to 1 m. Causes of limitations: economical consumption of covering material, ease of operation with precisely such film sizes, stability in strong wind. The standard width of a polyethylene film in rolls is usually 3 and 6 meters. Six-meter canvas can be cut in half and get from one purchase two sets of covering material for arc covers. The 3-meter width of the shelter is the most convenient and economical size for tunnel greenhouses of these parameters.
For growing seedlings and salads, small greenhouses are made in the shape of a square box up to half a meter high. They perform the function of portable structures: the seedlings of the transplanting period to a permanent place have reached - the greenhouse is transferred to another bed. Frame structures are also one of the types of portable greenhouses. Their dimensions range up to 1.2 m in width and 2 m in length. In frame buildings, one side along the length is often carried out inclined and folded back on the hinges, and set so that the slope is facing the southern (solar) side of the horizon.
By location
To get a good harvest, it’s not enough to decide on the type, size and material of greenhouses. It is important to choose their location on the summer cottage.
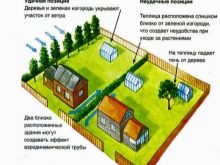
It is undesirable to place greenhouses in the following places.
- Under fruit trees and near high plantings. There are two main reasons for this: shading from the sun and a high risk of damage to covering material and structural elements from falling from the branches of fruits and branches.
- At the fence, bushes and buildings that can block the structure from the influence of the sun for a long time.Plants all daylight should receive good sunlight. Light is needed for the quality and taste of vegetables and herbs.
- At a remote, inclined or low point of the plot. Greenhouses should stand as close as possible to the dwelling (ideally - attached to the house or other buildings on their southern sides) on a leveled, dry and high place.
- In places where the wind blows constantly. These can be places between two summer houses, strips of fruit trees, in which artificially created wind crops.
Optimal placement along the length of the greenhouse - from east to west. You should also place any beds on the site, regardless of the presence of covering structures on them. In this case, the plants get the maximum coverage during the day, without shading each other in the beds. Depth greenhouses are arranged in dry places where groundwater is far from the soil surface.
Popular models
To summer residents who trust more ready types of greenhouses from proven manufacturers, than their own ability to design them, we can recommend the following popular models that have a good rating and have received good reviews from grateful buyers (but with an indication andsome flaws).
- Snowdrop tunnel greenhouse. Modifications have a length of from three to eight meters. Arcs of plastic pipes that do not crack either from heat or cold. Covering material is Agrotex, which has proven itself in greenhouse vegetable growing. The value of this material is that it allows atmospheric water and fresh air to pass through, while maintaining a normal microclimate inside.
- Hotbed "Dayas." It has an arc structure and consists of sections, which is convenient for changing the length of the device. Plastic arcs are soldered to the covering material, thereby ensuring the stability of the structure. The length of the greenhouse - from 4 meters, width - 120 cm, height - 70 cm. According to reviews, it is easy to install and fold, but not very convenient to maintain (opens with difficulty, bad quality arcs, the structure requires weighting).
- Greenhouse from cellular polycarbonate "Lotos". It has a height of only 80 cm, width - 90 cm, and length - 2.1 meters. Conveniently opens on the principle of "breadbasket", made of polycarbonate. Durable and reliable portable product.
- Greenhouse "Butterfly". The frame is made of lightweight metal, instead of covering material - cellular polycarbonate.A convenient sidewall tilting system on each side provides easy access to the plants. Easy to fold and carry to any place. The length is up to 4 m and the height is 1.5 m. Among the shortcomings it requires additional reinforcement from the wind.
The main advantage of all the models listed is affordability (from 2,000 to 6,000 rubles). Cover materials are of good quality, and cellular polycarbonate with a careful attitude can last for about 10 years.
Beautiful examples
When arranging a greenhouse farm in the country should not forget about aesthetics. Factory greenhouses are made with an exposure of proportions, sizes and do not spoil the general appearance of the site. The situation is worse with home-made products: sometimes their appearance does not hold water: who is in that much and without any rules. But it happens the other way around, if the owner thoroughly and with soul approaches the matter. For example, the following homemade greenhouses.
Polycarbonate greenhouse with a metal profile frame and a rising roof.
Greenhouse sections with their soil, heating system, made of wood with polycarbonate frames.
Tilting greenhouse of tubular frame and reinforced film.
See how to make a greenhouse from polypropylene pipes with your own hands, in the next video.